Sun Poisoning: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Oct 02, 2023
Sun poisoning, which might invoke images of toxic reactions, refers to an intense sunburn resulting from prolonged exposure to harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. Understanding sun poisoning is essential for healthcare professionals and the general public, as the sun emits rays that can damage the skin.
What Is Sun Poisoning?
Sun poisoning, also known medically as polymorphic light eruption, occurs when the skin experiences extreme exposure to the harmful UV rays emitted by the sun. It's more severe than your typical sunburn, indicating that the body has been overly exposed to UV rays, leading to an inflammatory response. This condition showcases the body's heightened sensitivity to sunlight, resulting in symptoms extending beyond sunburn discomfort.
Types of Sun Poisoning
Different individuals exhibit varying responses to sun exposure, making it essential to identify the types of sun poisoning. Identifying the signs of sun poisoning is the first step toward seeking timely intervention:
- Phototoxic Reactions: Certain medications can increase sensitivity to sunlight, leading to what is known as a phototoxic reaction. This reaction can intensify the effects of sun exposure, bringing about severe symptoms that resemble those of sun poisoning.
- Photoallergic Reactions: Some people experience photoallergic reactions to sunlight, causing a rash or blisters. Correctly treating sun poisoning and sunburn requires distinguishing between the two.
- Polymorphic Light Eruption (PMLE): This type of sun poisoning is particularly prevalent among individuals with a heightened sensitivity to sunlight. It manifests through the development of sun poison blisters and rashes, often requiring medical attention.
Symptoms of Sun Poisoning
Recognizing the onset of sun poisoning is essential in effectively managing and addressing the condition. It is imperative to discern between the signs of sun poisoning and mild sunburn to ensure the administration of appropriate care.
Initial Signs
The initial signs of sun poisoning might resemble a regular sunburn, characterized by redness, pain, and swelling. These signs can manifest within 6 to 12 hours following UV exposure, making it essential to monitor any developments closely. Understanding the distinction between sun poisoning and sunburn is vital at this stage, as it guides the subsequent course of action and treatment.
Advanced Symptoms
As the condition advances, individuals may encounter more severe symptoms. The manifestation of sun poison blisters, severe pain, dehydration, fever, confusion, nausea, vomiting, headaches, dizziness, and fainting signal the progression from a mild sunburn to a more critical medical condition. Promptly recognizing these signs of sun poisoning is paramount, as it facilitates timely medical intervention, thus preventing further complications.
What Causes Sun Poisoning?
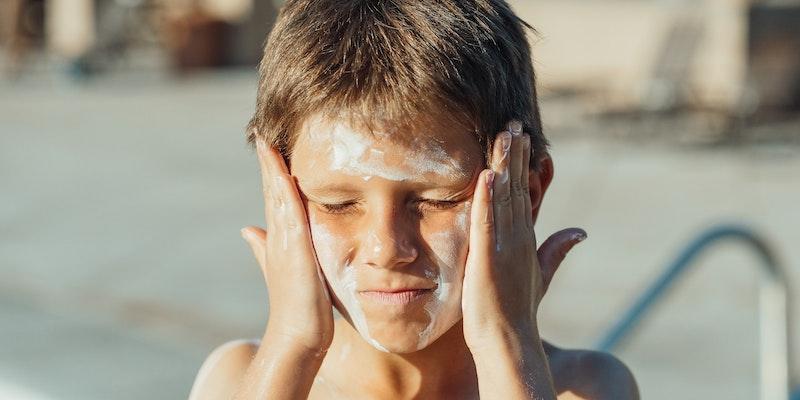

Understanding what causes sun poisoning is a foundational step in prevention and management. The primary trigger is extended exposure to the sun's UV rays, which can damage the skin, emphasizing the need to distinguish sun poisoning from sunburn for effective treatment.
UV Ray Exposure
Exposure to UV rays is the leading cause of sun poisoning. Extended periods in the sun without appropriate protection can lead to this condition, underscoring the importance of adopting preventive measures, such as applying sunscreen and wearing protective clothing.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors can increase an individual's susceptibility to sun poisoning. Recognizing these factors is vital for mitigating risks:
- Skin Type: Individuals with fair skin are more prone to developing sun poisoning.
- Family History: A family history of skin cancer can elevate the risk.
- Geographical Location: Residing in regions near the equator or at high altitudes can increase exposure to UV rays.
- Reflective Surfaces: Frequenting beaches or engaging in snow activities can intensify sunlight reflection, thereby heightening the risk.
- Medication and Supplements: Consumption of certain antibiotics, oral contraceptives, and herbal supplements like St. John's wort can increase sensitivity to sunlight.
Treatment Strategies for Sun Poisoning
Addressing sun poisoning effectively requires a multifaceted approach, considering the severity of the condition. Incorporating appropriate treatments can alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications, especially when the signs of sun poisoning are identified early.
Immediate Relief Measures
Immediate relief measures are indispensable in treating sun poisoning. These may include:
- Cool Compresses: Applying cool compresses to the affected areas can relieve pain and swelling.
- Hydration: Replenishing fluids is vital to counteract dehydration resulting from sun poisoning.
- Rest: Adequate rest is essential to facilitate the body's healing process.
Medical Interventions
Depending on the severity, medical interventions may be necessary. In cases where sun poison blisters are present, healthcare providers might prescribe topical antibiotics to prevent infection. Other potential treatments include:
- Steroid Creams: Topical steroids can be beneficial for severe inflammation and pain.
- Oral Steroids: These may be prescribed to reduce systemic inflammation and discomfort.
- IV Fluids: In cases of severe dehydration, intravenous fluids may be administered to restore the body's fluid balance.
Long-term Management
Recognizing the signs of sun poisoning and implementing preventive strategies are crucial for long-term management. This involves regular use of sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding prolonged exposure to direct sunlight, particularly during peak hours.
Potential Complications of Sun Poisoning
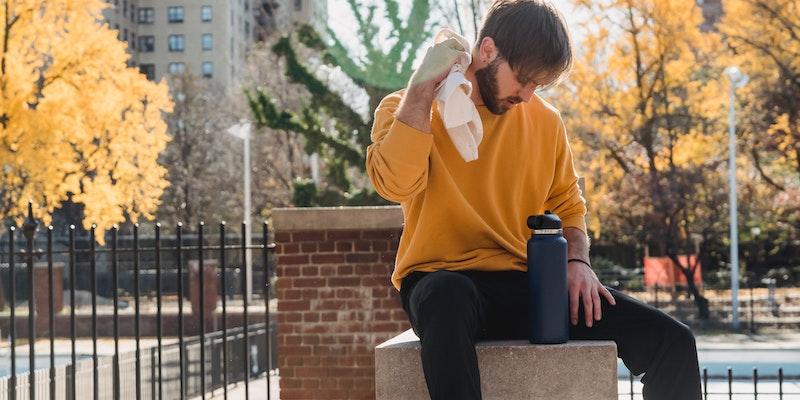

Left unaddressed, sun poisoning can lead to many complications, underscoring the importance of promptly distinguishing sun poisoning from sunburn. Early identification and treatment of the signs of sun poisoning are essential in mitigating risks associated with this condition.
Infection
One of the primary complications of sun poisoning is infection. Sun poison blisters and damaged skin serve as entry points for bacteria, necessitating prompt treatment to prevent the spread of disease. Signs of an infection include oozing, red streaks, and increased pain.
Dehydration
Sun poisoning often causes dehydration, so drink enough. Severe dehydration can cause significant health complications, requiring quick medical attention.
Long-term Skin Damage
Sun poisoning can damage the skin permanently. Severe sunburns increase the risk of wrinkles and sunspots. Due to the high risk of skin cancer, skin changes must be regularly monitored.
Psychological Impact
The experience of sun poisoning can also have a psychological impact, particularly in cases where the physical symptoms are severe and prolonged. Individuals need to seek support and employ coping mechanisms to address any emotional distress associated with the condition.